Morgan Stanley
Though Morgan Stanley‘s Innovation Lab sits firmly in Manhattan’s Financial District, I hardly saw any of the finance bros who dot the streets outside during my recent tour.
I didn’t know quite what to expect ahead of my visit — robots analyzing market moves? intricate gadgets? — and Megan Brewer, the head of firmwide market innovation and labs, tempered my wildest expectations when she described the space as “effectively a very large data center.” The lab, she said, gives people “all the infrastructure that is needed to test ideas in a secure, scalable fashion.”
Morgan Stanley employees who want to experiment with their own ideas or test third-party products that might help the firm can use the Innovation Lab. Brewer told me that most of the people who use the space are technologists, but that everyone at the bank has access.
“Most people don’t think of banks as where people are sitting there soldering and working on custom design trips,” she said. “But we offer that as well.”

Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is sure to celebrate innovators
And it became clear to me that Brewer’s team is pulling multiple levers to attract and retain the firm’s technologists. She helps run the bank’s Patent Accelerator Program, which guides innovators through the patent process. When someone’s invention earns a patent, Brewer’s team sends a message to their manager. They post on internal sites, frame the physical patent, and note the accomplishment on the person’s company profile. Morgan Stanley has even put patent-holders’ faces on their digital ads in Times Square, Brewer said.
Patents don’t only grant legal control over an invention, but also acknowledge something as a creative, genuinely new idea. Inventions have to be “non-obvious” to get a patent, and they’re a quantitative way for banks to flex their technological chops.
Banks are generally racing to embrace the newest technology. A McKinsey report from late 2024 found that banks have massively increased their tech spending in recent years, and are especially focused on hiring people to produce products in-house.
While tech companies are cutting back on new-hire offers, my time at Morgan Stanley made it clear that banks might be keen on snapping up some of the available talent. Citi also has a network of physical innovation labs across the world, and many banks have accelerator or innovation programs.
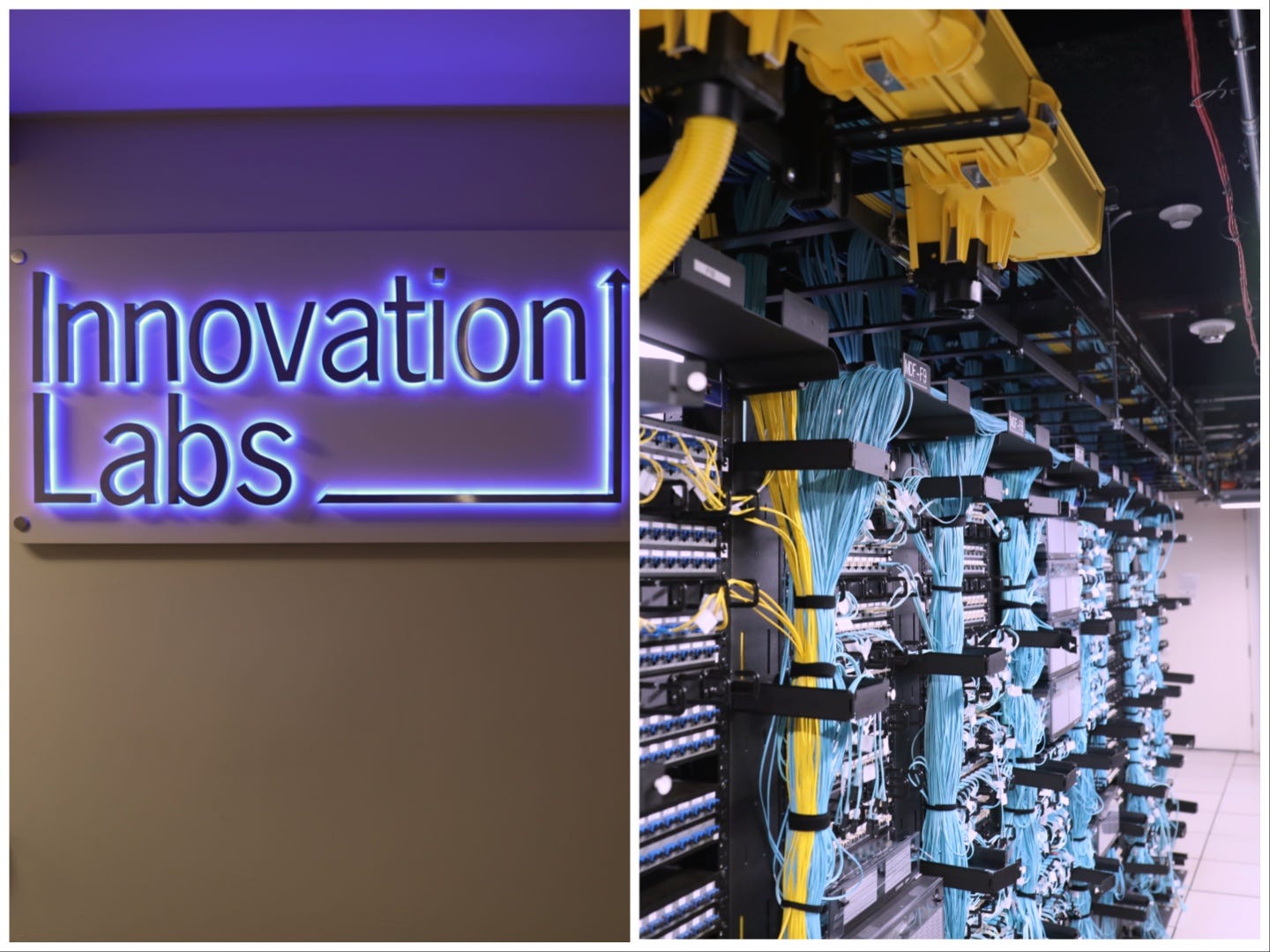
When we were ready to enter the lab, Brewer told me I might need to leave my notebook behind, since it’s flammable. The first room, though, seemed pretty innocuous: a bunch of computers with black screens, and a lone guy sitting at a desktop. I almost felt like I was in a “Black Mirror” episode, the rows of blank monitors a dystopian end-of-world tableau.
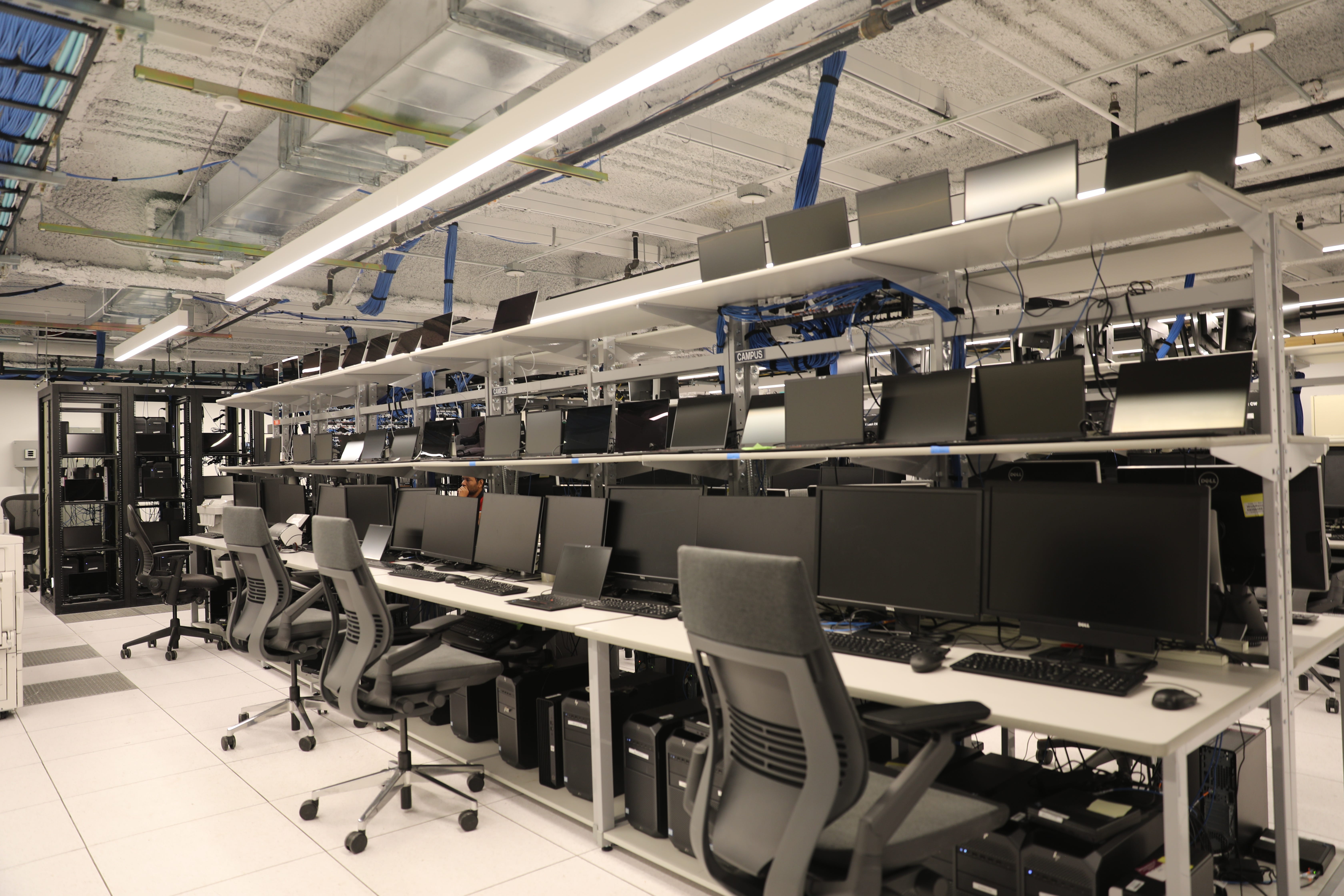

Morgan Stanley
The lab was full of high-end, deceptively plain machines
As we kept moving through the lab, the image of a stereotypical bank continued to fade. It was hot and loud inside the data center, with a white noise of whirring machines and fluorescent lighting. Brewer advised me to stand on a vent if I got too hot amid the rows of equipment.
Most of the time, I didn’t know what I was looking at — at one point, it turned out to be the lab’s first GPU. I asked how much it was all was worth, and everyone laughed, saying I didn’t want to know.
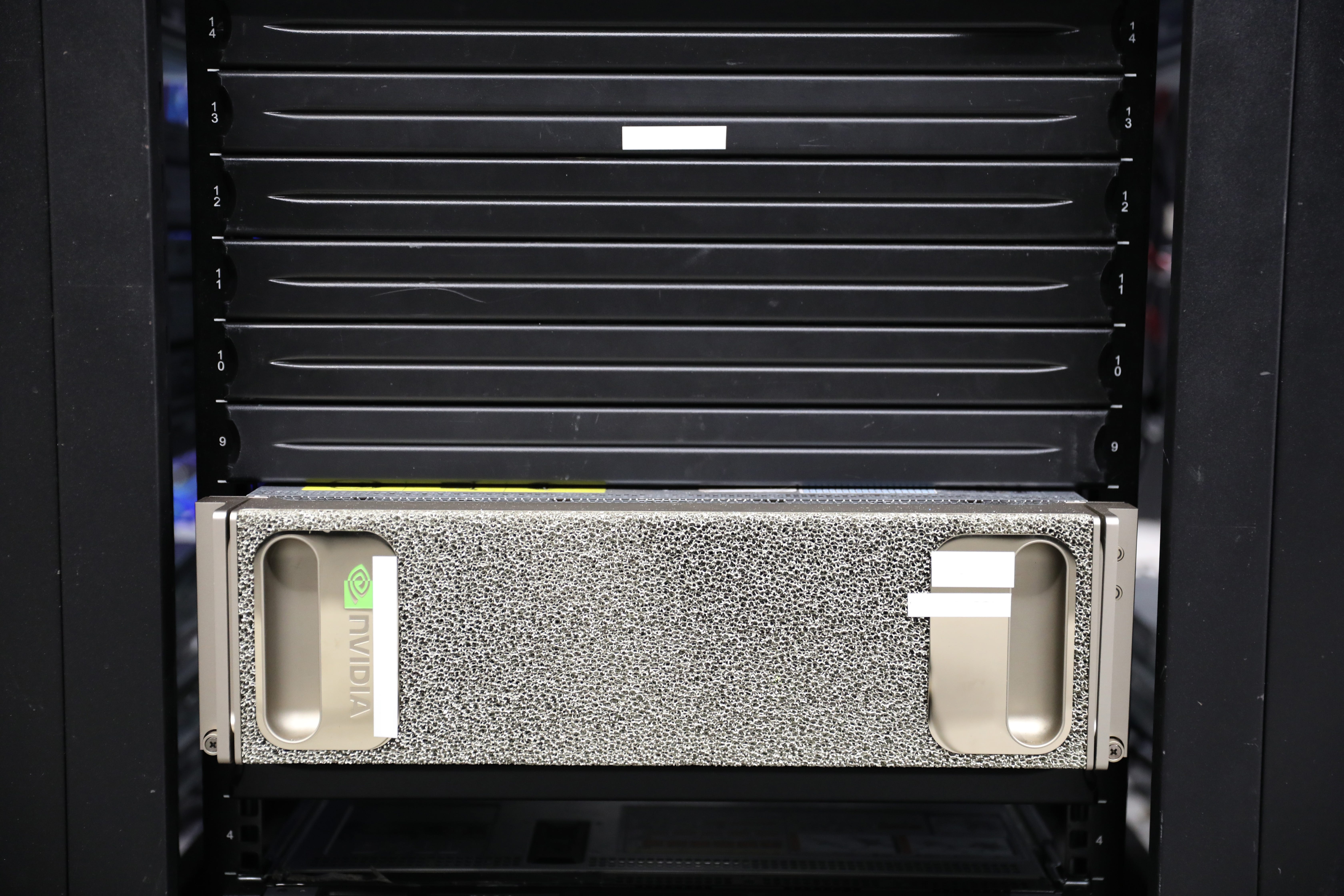

Morgan Stanley
“Many millions,” Brewer said, adding that some pieces cost as much as rent on a New York City apartment. (I became very conscious of not stepping on the many blue wires grazing the floor in my kitten heels.)
Huge investment aside, though, some parts of the lab seemed almost scrappy, evidence of exploration and technology that’s still in the works. There were labels made of blue tape and Sharpie, stickers that looked like they came from a name-tag machine, flame-retardant Post-Its.
At the end of the tour, I met an electrical engineer, who was standing in front of a clearly very complex, very impressive machine he’d made. My tour guide told me that he’d already built and patented multiple versions of the chip machine sitting before us, which he was too polite to mention himself.
He carefully explained his project — Morgan Stanley asked that don’t get into specifics here — and indulged my many questions, talking to me in what were likely excruciatingly simple terms. When I asked whether he ever expected to work at a bank, I got an emphatic no and some knowing head-nods from those leading my tour.
Morgan Stanley has around 23,000 tech employees, 15,000 of whom are developers. At the time of this writing, the bank had 249 full-time technology jobs listed on its site.
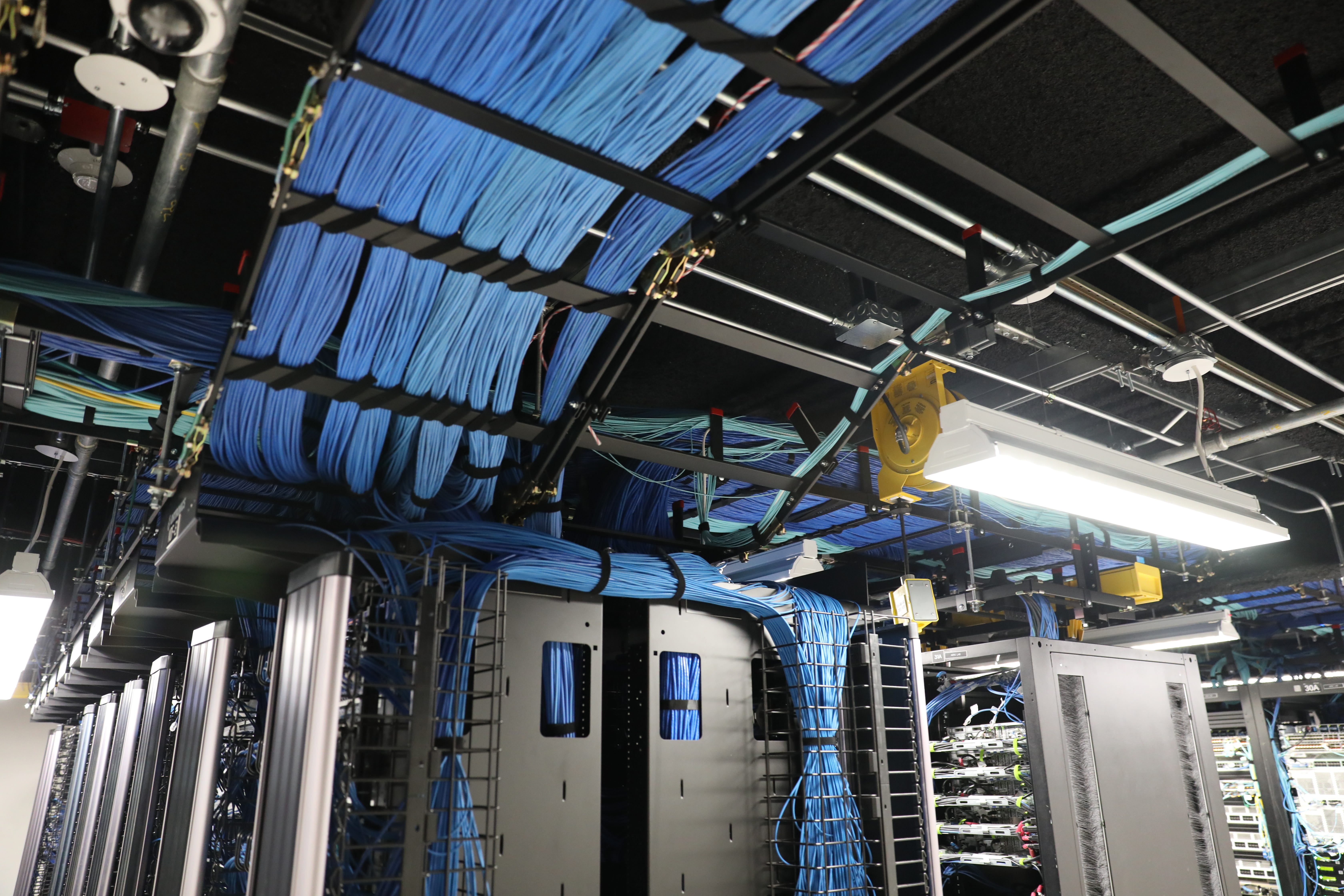

Morgan Stanley
The lines between banking and Big Tech
I didn’t talk to, or maybe even see, a single banker the whole time I was there, which makes some sense given that Morgan Stanley’s main New York headquarters are in Midtown and I was at a smaller office downtown. People talked in the terms of a startup, pushing themes like innovation that may appeal to an engineer more than the average investment banker.
We eventually left the lab and emerged into a similarly harshly lit hallway, the walls lined with cardboard boxes, before passing through a door and into the shinier, more central office area. I stepped into the bathroom before leaving; it was designed in the crisp image of the finance aesthetic, with a few cubbies holding hair straighteners.
Looking around, I remembered where I was: a bank at the tip of Manhattan, not a tech company in California. I wondered, though, how the lines between the two will continue to blur — and how much they’ve blurred already.
The post I toured Morgan Stanley’s Innovation Lab and saw firsthand how banks are trying to pull top tech talent appeared first on Business Insider.




