For the past two-and-a-half decades, the mandate for global business leaders was relatively straightforward: grow the existing business, allocate capital efficiently, and implement technology to drive productivity. But Mohamed Kande, global chairman of PwC, speaking to Fortune in Davos, Switzerland, ahead of the World Economic Forum’s annual meeting, insisted that era is over. Kande argued that the CEO job has changed more in the past year than anything he’s seen over the last quarter-century.
“This is one of the most testing moments for leaders,” Kande told Fortune‘s Diane Brady, describing a new “tri-modal” mandate that requires executives to simultaneously run their current business, transform it in real time, and also build entirely new business models for the future. “I’ve not seen that in 25 years,” he said.
Despite this pressure, Kande’s message to the global business community is rooted in historical optimism. “Do not fear the future. It is unsettling. It is true. Every day something changes, but do not fear it,” he said, noting that all the uncertainty so stressful to executives has happened before, from tariffs, roughly 100 years ago, to the industrial revolution, even further back. “Eventually, something good will happen.” Kande allowed that he’s an optimist by nature, but he insisted that top leaders can adjust to this business climate.
The AI Execution Gap
Of course, a primary driver of this unsettling change is the rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), as revealed in PwC’s 29th global CEO survey, “Leading Through Uncertainty in the Age of AI,” released at the onset of the annual meeting in Davos. Based on responses from 4,454 CEOs across 95 countries and territories, the survey reveals a stark disconnect between ambition and reality. Kande said the business community made huge strides from 2024 to 2025, going from asking themselves whether they can or should adopt AI to a point where “nobody is asking that question anymore. Everybody’s going for it.”
PwC’s survey finds, however, that only 10% to 12% of companies report seeing benefits on the revenue or cost side, while a staggering 56% say they are getting “nothing out of it.” This echoes the MIT study that shook markets in August with the finding that 95% of generative AI pilots were failing across the corporate sector.
Kande attributed this tension not to the technology itself, but to a lack of foundational rigor. “Somehow AI moves so fast … that people forgot that the adoption of technology, you have to go to the basics,” he explained, citing the need for clean data, solid business processes, and governance. PwC is finding that the companies that are seeing benefits from AI are “putting the foundations in place.” It’s about execution, not technology, he argued, and that comes down to good management and leadership.
The Confidence Paradox and U.S. Dominance
The uncertain environment has also created a paradox in business sentiment, Kande told Fortune. While CEOs express confidence in the global economy, only 30% have confidence that they can grow their own businesses. Kande questioned whether this hesitation stems from geopolitics, tariffs, technology, or a lack of leadership agility. The last 15 years, he noted, have been ones of solid growth and stable business models, making this time a real test for the C-suite. “This is one of the most testing moment for leaders, what we have today,” he said, because it requires the ability to change fast and adapt quickly without getting bogged down in day-to-day, tactical combat.
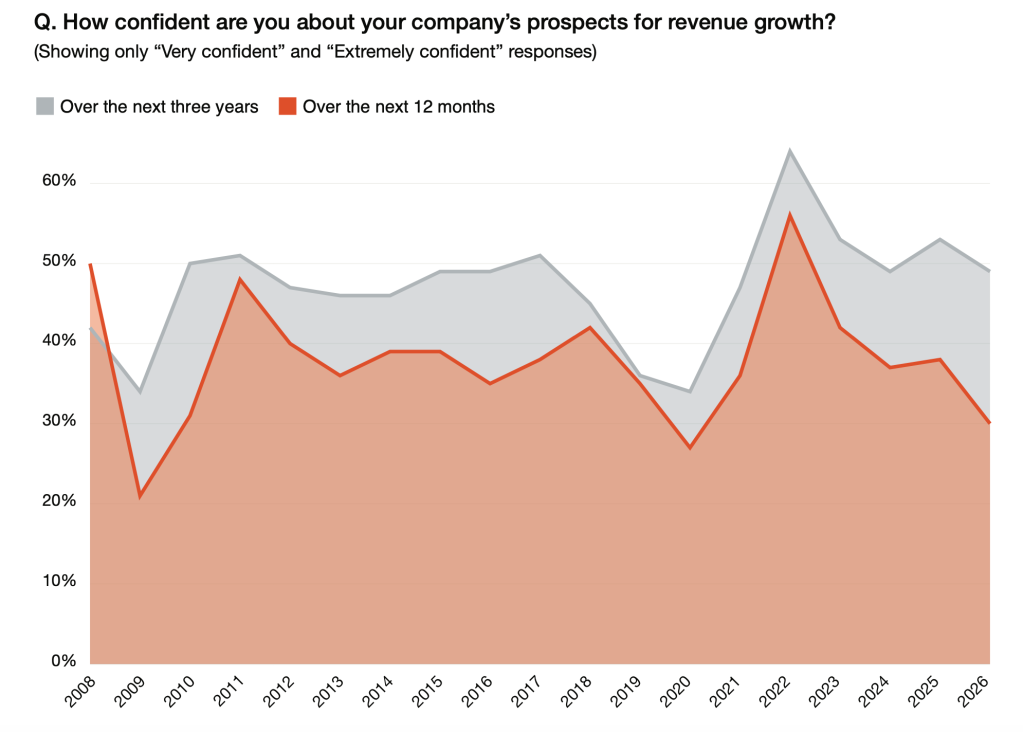
Only three in 10 CEOs were confident in PwC’s 29th survey about revenue growth over the next 12 months, down from 38% in 2025 and 56% in 2022, marking a five-year low in CEO confidence in their own revenue outlook. Another survey question may be more revealing, about CEO confidence in their company’s 12‑month revenue growth: this has fallen sharply over recent years, even as many leaders continue to pursue multiyear opportunities to reinvent their businesses through AI, innovation, and cross-sector expansion.
The transformation of the CEO role is trickling down to the workforce, necessitating a reimagining of career paths. Kande warned that the traditional “apprenticeship model”—where entry-level employees learn by doing basic tasks—is being disrupted by AI. That classic career ladder, starting at the entry level, taught lots of expertise through hands-on learning, but this will have to be redesigned, going forward, to teach “system thinking” rather than task execution, as AI increasingly handles the latter.
Ultimately, Kande urges executives to look at the last 50 to 100 years rather than the last five to understand the current moment. Citing the infrastructure booms of the railroad era and the early internet, he said he believes the current wave of investment will birth the next age of innovation. The CEO survey’s framing of a coming “decade of innovation and industry reconfiguration” supports this long-term view, highlighting that companies generating more revenue from new sectors tend to enjoy higher profit margins and higher CEO confidence in future growth.
“I’m an optimist,” Kande concluded. Rather than being afraid of all of the changes that are happening now, he urged leaders to remember that people fear what they don’t understand, and the best remedy for that is to seek understanding. “That’s why I spend so much time learning now and traveling a lot, just to understand what’s happening and thinking about what can be done differently. That’s why I don’t fear AI.”
“I’ve seen change,” Kande said. “You’ve got to embrace it.”
The post PwC’s global chairman says most leaders have forgotten ‘the basics’ as 56% are still getting ‘nothing’ out of AI adoption appeared first on Fortune.




