Around 1915, the last known Chumash basket maker, Candelaria Valenzuela, died in Ventura County, and with her went a skill that had been fundamental to the Indigenous people who lived for thousands of years in the coastal regions between Malibu and San Luis Obispo.
A century and two years later, 70-year-old Santa Barbara native Susanne Hammel-Sawyer took a class out of curiosity to learn something about her ancestors’ basket-making skills.
Hammel-Sawyer is 1/16 Chumash, the great-great-great-granddaughter of Maria Ysidora del Refugio Solares, one of the most revered ancestors of the Santa Ynez Band of Chumash Indians for her work in preserving its nearly lost Samala language.
But Hammel-Sawyer knew nearly nothing about Chumash customs when she was a child. As a young mother, she often took her four children to the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, where she said she loved to admire the museum’s extensive collection of Chumash baskets, “but I had no inkling I would ever make them.”
Nonetheless, today, at age 78, Hammel-Sawyer is considered one of the Santa Ynez Band’s premier basket makers, with samples of her work on display at three California museums.
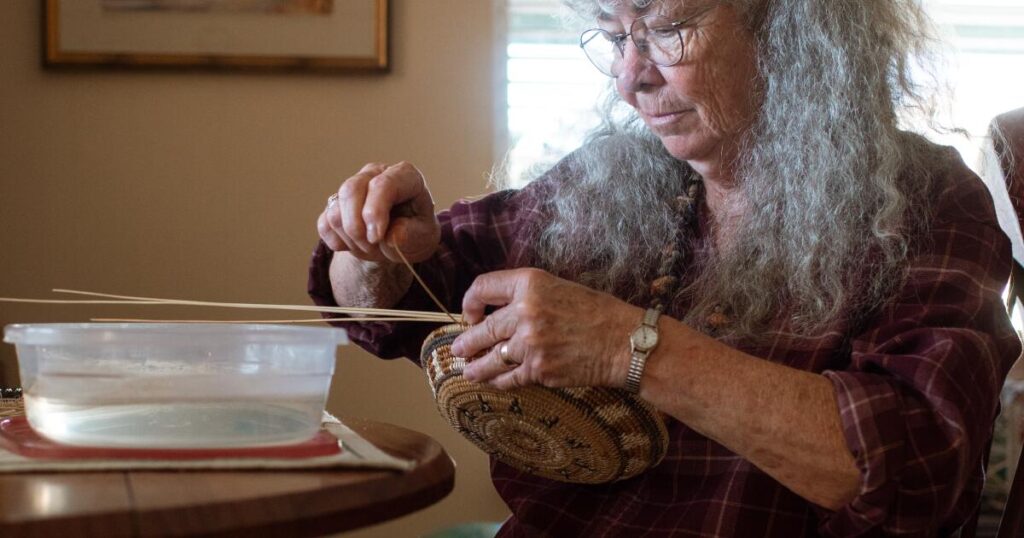
She grows the basket rush (Juncus textilis) reeds that make up the weaving threads of her baskets in a huge galvanized steel water trough outside her Goleta home and searches in the nearby hills for other reeds: primarily Baltic rush (Juncus balticus) to form the bones or foundation of the basket and skunk bush (Rhus aromatica var. trilobata) to add white accents to her designs.
All her basket materials are gathered from nature, and her tools are simple household objects: a large plastic food storage container for soaking her threads and the rusting lid of an old can with different-sized nail holes to strip her reeds to a uniform size. Her baskets are mostly the yellowish brown color of her main thread, strips of basket rush made pliant after soaking in water.
The basket reeds often develop a reddish tint at the bottom part of the plant when they’re drying. “Those are my gold,” she said, because she uses those short ends to add reddish designs. Or sometimes she just weaves them into the main basket for added flair.
The only other colors for the baskets come from skunk bush reeds, which she has to split and peel to reveal the white stems underneath, and some of the basket reeds that she dyes black in a big bucket in her backyard.
“This is my witches’ brew,” she said laughing as she stirred the viscous inky liquid inside the bucket. “We have to make our own from anything with tannin — oak galls, acorns or black walnuts — and let it sit to dye it black.”
Hammel-Sawyer is remarkable not just for her skill as a weaver, but her determination to master techniques that went out of practice for nearly 100 years, said anthropologist and ethnobotanist Jan Timbrook, curator emeritus of ethnography at the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, which claims to have the world’s largest museum collection of Chumash baskets.
“Susanne is one of the very few contemporary Chumash people who have truly devoted themselves to becoming skilled weavers,” said Timbrook, author of “Chumash Ethnobotany: Plant Knowledge Among the Chumash People of Southern California.” “Many have said they’d like to learn, but once they try it and realize how much time, patience and practice it requires … they just can’t keep it up.”
In her eight years, Hammel-Sawyer has made just 34 baskets of various sizes (she’s close to finishing her 35th), but she’s in no hurry.
“People always ask how long it takes to make a basket, and I tell them what Jan Timbrook likes to say, ‘It takes as long as it takes,’” Hammel-Sawyer said. “But for me, it’s a way of slowing down. I really object to how fast we’re all moving now, and it’s only going to get faster.”
She and her husband, Ben Sawyer, have a blended family of five children and nine grandchildren, most of whom live near their cozy home in Goleta. Family activities keep them busy, but Hammel-Sawyer thinks it’s important for her family to know she has other interests too.
“When you’re older, you have to be able to find a passion, something your children and grandchildren can see you do, not just playing golf or going on cruises, but doing something that matters,” she said. “I wish my grandmother and my father knew I was doing this because it’s a connection with our ancestors, but it’s also looking ahead, because these baskets I’m making will last a very long time. It’s something that comes from my past that I’m giving to family members to take into the future, so it’s worth my time.”
Also, this isn’t a business for Hammel-Sawyer. Her baskets are generally not for sale because she only makes them for family and friends, she said. The baskets at the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History and the Santa Ynez Chumash Museum and Cultural Center belong to family members who were willing to loan them out for display. The Chumash museum does have some of Hammel-Sawyer’s baskets for sale in its gift shop, which she said she reluctantly agreed to provide after much urging, so the store could offer more items made by members of the Band.
The only other basket she’s sold, she said, was to the Autry Museum of the American West, because she was so impressed by its exhibits involving Indigenous people. “I just believe so strongly in the message the Autry is giving the world about what really happened to Indigenous people, I thought I would be proud to have something there,” she said.
Making a basket takes so long, Hammel-Sawyer said, that it’s important for her to focus on the recipient, “so while I’m making it, I can think about them and pray about them. When you know you’re making a basket for someone, it has so much more meaning. And I’m so utilitarian, I always hope someone will use them.”
For instance, she said, she made three small baskets for the children of a friend and was delighted when one used her basket to carry flower petals to toss during a wedding. Almost any use is fine with her, she said, except storing fruit, because if the fruit molds, the basket will be ruined.
Baskets were a ubiquitous part of Chumash life before the colonists came. They used them for just about everything, from covering their heads and holding their babies to eating and even cooking, Timbrook said. They put hot rocks into their tightly woven baskets, along with food like acorn mush, to bring the contents to boil.
“People think pottery is a higher form of intellectual achievement, but the thing is, baskets are better than pottery,” Timbrook said. “They’ll do anything pottery will do; you can cook in them and store things in them, and when you drop them, they don’t break.”
After Hammel-Sawyer’s first marriage ended, she worked as an assistant children’s librarian in Santa Barbara and met a reference librarian named Ben Sawyer. After their friendship turned romantic, they married in 1997 and moved, first to Ashland, Ore., then Portland, and then the foothills of the Sierras in Meadow Valley, Calif., where they took up organic farming for a dozen years.
Meadow Valley’s population was 500, and the big town was nearby Quincy, the county seat, with about 5,000 residents, but it still had an orchestra and she and her husband were both members. She played cello and he viola, not because they were extraordinary musicians, she said, but because “we played well enough, and if we wanted an orchestra, we would have to take part. I loved how strong people were there. We were all more self-sufficient than when we lived in the city.”
The Sawyers moved back to Santa Barbara in 2013, the year after her father died, to help care for her mother, who had developed Alzheimer’s disease. And for the next four years, between caring for her mother, who died in 2016, and the birth of her grandchildren, family became her focus.
But in 2017, the year she turned 70, Hammel-Sawyer finally had the space to begin looking at other activities. Being she’s 1/16 Chumash, she was eligible for classes taught by the Santa Ynez Band. She had seen several class offerings come through over the years, but nothing really captured her interest until she saw a basket-weaving class offered by master basket maker Abe Sanchez, as part of the tribe’s ongoing effort to revive the skill among its members.
Most Chumash baskets have some kind of pattern, although today people have to guess at the meaning of the symbols, Timbrook said. Some look like squiggles, zigzaggy lightning bolts or sun rays, but the wonder, marveled Hammel-Sawyer, is how the makers were able to do the mental math to keep the patterns even and consistent, even for baskets that were basically everyday tools.
Hammel-Sawyer is careful to follow the basics of Chumash weaving, using the same native plants for her materials and weaving techniques that include little ticks of contrasting color stitches on the rim, something visible in most Chumash baskets. She keeps a good supply of bandages for her fingers because the reeds have sharp edges when they’re split, and it’s easy to get the equivalent of paper cuts.
She keeps just two baskets at her house — her first effort, which “wasn’t good enough to give anybody,” she said, laughing — and a basket hat started by her late sister, Sally Hammel.
“Sally was an artist in pottery, singing, acting and living life to the fullest,” Hammel-Sawyer said, and she was very excited to learn basketry. Her basket hat started well, but about a third of the way in, she got cancer “and her stitches became more and more ragged. She had trouble concentrating, trouble preparing materials,” Hammel-Sawyer said. “Everything became so difficult that she hid the basket away. I know she didn’t even want to look at it, let alone have anyone else see it.”
After her sister died in 2020, Hammel-Sawyer had a hard time finding the basket, “but I did, and I asked my teacher what to do, and he said, ‘Just try to make sense of her last row’ … So that’s what I did.” She added a thick black-and-white band above the ragged stitches and finished the blond rim with the traditional contrasting ticking.
The hat rests now above the window in Hammel-Sawyer’s living room, except when she wears it to tribal events.
“Sally and I were very close, and I think she’d just be happy to know it was finished and appreciated,” Hammel-Sawyer said. “Even the hard parts … deeply appreciated.”
The post At 70, she embraced her Chumash roots and helped revive a dying skill: basketmaking appeared first on Los Angeles Times.