A team of marine mammal experts had spent several days in Cowichan Bay, British Columbia, searching for a sea lion with an orange rope wrapped around its neck. As the sun set on Dec. 8, they were packing up, for good, when a call came in.
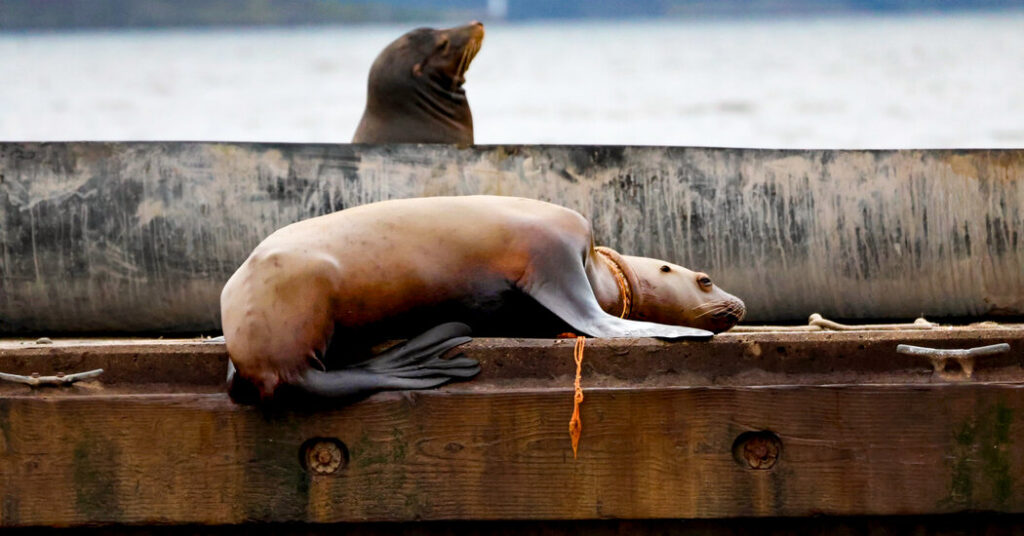
The tangled animal, a female Steller sea lion weighing 330 pounds, had been spotted on a dock in front of an inn, leading into the bay in southwestern Canada.
The rope was wrenched four times around her neck, carving a deep gash. Without help, the sea lion would die.
The team had been trying to find the sea lion for a month, and on that day, with daylight running out, the nine members that day knew they needed to work fast. They relaunched their boats and a team member loaded a blow gun and shot her with a sedative.
“Launching the dart is the easiest part of the whole operation,” said Dr. Martin Haulena, executive director of the Vancouver Aquarium Marine Mammal Rescue Society, which conducted the rescue alongside Fisheries and Oceans Canada. “It’s everything that happens after that, that you just have no control over.”
Steller sea lions, also known as northern sea lions, are the largest such breed. They are found as far south as Northern California and in parts of Russia and Japan. A male Steller sea lion can weigh up to 2,500 pounds.
The Cowichan Tribes Marine Monitoring Team assisted the rescue society, calling it whenever the sea lion was spotted. The tribe named her Stl’eluqum, meaning “fierce” or “exceptional” in Hul’q’umi’num’, an Indigenous language, according to the rescue society.
After Stl’eluqum was sedated, she jumped from the dock into the water. Recent torrential rains and flooding had stirred up debris, making the water brown, and harder to spot the sea lion, Dr. Haulena said.
Several minutes after the sea lion dived into the bay, the drone spotted her and the team moved in.
The rope had multiple strands and it was wrapped so deeply that she most likely wasn’t able to eat, Dr. Haulena said. At first, the team had trouble freeing her.
“You couldn’t see it because it was way dug in underneath the skin and blubber of the animal,” Dr. Haulena said.
After unraveling the rope, the team tagged her fin, gave her some antibiotics and released her.
Freeing the sea lion was the culmination of weeks of searching and missed moments. The first call about the tangled marine mammal was made to the Fisheries and Oceans Canada hotline on Nov. 7, according to a news release from the rescue society. Then the society logged more calls.
The Vancouver Aquarium Marine Mammal Rescue Society, a nonprofit that works in partnership with the Vancouver Aquarium, searched for several days for the sea lion. The day they found her was the last of the rescue effort because bad weather was forecast for the area around the bay. The call that led them to Stl’eluqum came from the Cowichan Tribes, Dr. Haulena said.
The society, Dr. Haulena said, cares for about 150 marine mammals from its rescues every year — sea lions, otters, harbor seals and the occasional sea turtle. The group gives medical care to animals it takes in, such as Luna, an abandoned newborn sea otter who was three pounds when she was found and still had her umbilical cord attached.
Many of the society’s rescues involve animals tangled in garbage or debris, Dr. Haulena said.
Stl’eluqum was tangled in nylon rope commonly used to tie boats or crab traps, he said. When sea lions get something caught around their necks it can grow tighter until it cuts into their organs, sometimes fatally, he said.
“It’s our garbage; it’s our fault,” Dr. Haulena said. “It’s a large amount of animal suffering and not a good outcome unless we can do something.”
Rylee Kirk reports on breaking news, trending topics and major developing stories for The Times.
The post Team Races Against Time to Save a Tangled Sea Lion in British Columbia appeared first on New York Times.